Kargil War | India Pakistan Kargil war 1999 | Who Won The Kargil War ?
Table Of Contents
- Kargil war Facts
- Jammu And Kashmir History.
- What is the Kashmir Issue .
- History Of India Pakistan Wars.
- Kargil War Location
- Who Started the Kargil war
- Main Objective Of the kargil War for Pakistan
- Indian Army Operation In Kargil War.
- Indian Air Force operation In Kargil war
- Kargil War Heroes And Gallantry Awards
- Who Won the kargil war ?
- International Reaction to Kargil war
- Political Fallout Of Kargil War
- Important Lessons Of kargil War
- Conclusion
Kargil War Facts
The Kargil War was the fourth armed conflict fought between India and Pakistan in Year 1999. The kargil war was started by Pakistan when Pakistani soldiers crossed the LOC ( Line Of Control ) disguised as militants , intruded into the Indian territory and occupied the Indian posts left vacant by the Indian army .
Indian Army launched a massive counterattack to evict the Pakistani soldiers. The war lasted for almost two months and the Indian army decisively won the kargil war and recovered all the Indian posts occupied by the Pakistani soldiers. Pakistan was once again defeated in this war and had to retreat back to the original LOC – line of control position.
The main cause of Kargil war was the Pakistani obsession for the control over Kashmir against the wishes of Kashmiri people. India and Pakistan have fought four wars since independence on Kashmir issue. Pakistan has attacked India four times after the independence over the Kashmir issue and lost all four wars with India .
The Kargil war was the fourth war started by Pakistan as an attempt to compel India to settle the Kashmir issue on Pakistan’s terms. In order to understand the chain of events that led to the Kargil war over Kashmir issue , we need to look back in the history of Kashmir and India, necessary to put the things in the right perspective.

Watch Most Comprehensive Coverage Of Kargil War
Jammu And Kashmir History
During the first millennium, the Kashmir used to be an important centre of Hinduism. Later of Buddhism also came to Kashmir. The Islamization of Kashmir took place during the 13th and 15the century. Subsiquently , the Mughal rule prevailed over Kashmir till 1751 .
The Leader of Sikh empire Ranjit Singh annexed Kashmir in 1846 and his rule came to an end with the advent British East India Company. Prior to independence Kashmir was an independent princely state .

After India’s independence in 1974 , the ruler of Kashmir Maharaja Hari Singh decided to join India. On October 27, 1947, Maharaja Hari Singh signed the “Instrument of Accession” with India and that was accepted by India’s last Governor-General Lord Mountbatten. And Kashmir successfully acceded to India in 1947.
Just after Maharaja Hari Singh’s decision to accede Kashmir to India, Pakistan had sent its armed forces to capture the Kashmir. However, this Pakistani attack was defeated by India. India had sent and deployed its army to protect Kashmir from the Pakistani invasion of Kashmir. This war between India and Pakistan is also referred to as the First Kashmir war in 1947.
Kashmir History
Watch Kashmir history And how it is related to Kargil War
End Of British Rule – Independence Of India And Pakistan 1947
India used to be a British colony before its independence prior to 1947 . The British ruled India for two centuries. The Indian freedom struggle movement led by Mahatma Gandhi, Indian National Army led by Netajee Subhash Chandra Bose and other prominent leaders played a crucial role to end the British rule over India . Finally, India became independent in 1947.
During India’s independence , The British decided to partition India into two countries and created Pakistan as an independent state. The large chunk of the Muslim population joined the newly created Pakistan and the remaining population which includes Hindus , Christians, Sikhs and other minority population joined India.
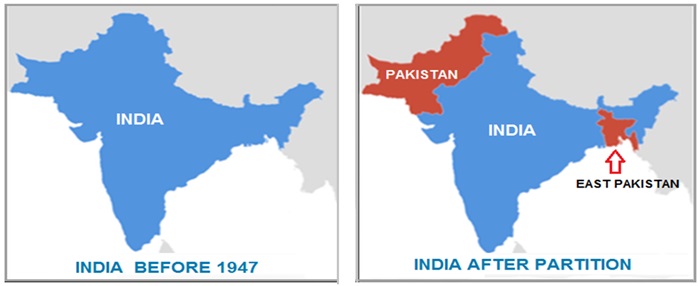
What is the Kashmir Issue ?
Kashmir was an independent princely state prior to India’s independence. Kashmir became a princely state after the British acquired Kashmir on 16th March 1846 . British sold Kashmir to Maharaja Gulab Singh and subsequently, Maharaja Hari Singh inherited Kashmir being the great-grandson of Maharaja Gulab Singh.
Kashmir being a majority Muslim populated , Pakistan’s founder Mohammed Ali Jinha wanted Kashmir to be a part of Pakistan against the wishes of Maharaja Hari Singh and the people of Kashmir.
Pakistan refused to accept the Maharaja Hari Sing’s decision to join India . Pakistan sent its armed troops disguised as a tribal invasion to capture the Kashmir. However, India had sent its army to secure the Kashmir from Pakistani invasion. This war continued for a year and eventually, a cease-fire agreement was reached between India and Pakistan with the intervention of the United Nations.
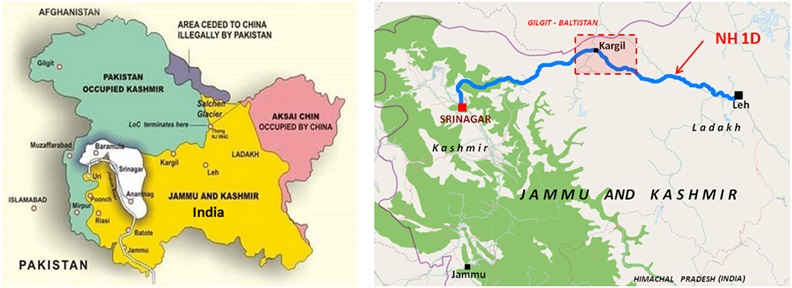
Despite UN resolution dated 13th August 1948 , Pakistan still continues to occupy some area Kashmir which is referred as POK ( Pakistan Occupied Kashmir ) and the remaining area continues to be under Indian control.

History Of India Pakistan wars
After independence in 1947 onwards , India and Pakistan have fought four wars over Kashmir issue . All these four armed conflicts were started by Pakistan .
- First War Of Kashmir 1947
- Second India Pakistan War 1965
- Third India Pakistan Bangladesh Liberation War 1971.
- Fourth India Pakistan Kargil War 1999.
First War Of Kashmir 1947 :
In this war, Pakistani forces attacked Indian Kashmir just after independence. This War ended after UN Intervention 1948 . Indian army defeated Pakistani forces attempt to capture the Kashmir.
Second India Pakistan War 1965 :
In this war Pakistani forces attacked India to capture India . Indian armed forces successfully defeated Pakistani forces.
Third India Pakistan Bangladesh Liberation War 1971 :
In this war, Pakistan launched an attack on India . India defeated Pakistan and liberated East Pakistan as an independent country Bangladesh. Lieutenant General Jagjit Singh Aurora of Indian Army and Pakistan’s Lieutenant General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi signed the “Instrument of Surrender” along with the surrender of 93000 Pakistani soldiers surrendered.

Forth India Pakistan Kargil war :
In this war, Pakistan again attempted to capture Indian territory in Kargil district in Jammu & Kashmir state. Pakistani soldiers crossed the LOC ( Line Of Control ) disguised as militants . India responded with major military action against Pakistani intruders and defeated Pakistan in Kargil war. All the Pakistani intruders were evicted after an intense battle on the most difficult hilly terrain of Kargil district.
Kargil War Location
The Kargil is located along the India Pakistan LOC – Line of Control which is a defacto boundary which bifurcates Indian And Pakistan administered Kashmir. The Kargil is a small town in the Kargil district of Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir state of India.
Kargil is a strategically important because National highway NH-1D passes through Kargil which connects Shrinagar to Leh . This is a very important road link for the Indian army which is used to provide the logistical support to the Indian troops deployed in Siachen area.
Who Started The Kargil War ?
Pakistan started the Kargil war by sending its army soldiers disguised as militants and occupying the vacant Indian post usually left unguarded every winter. It is a usual practice by both the armies to vacate the forward posts along the LOC on the mountain peaks in winter due to extreme weather conditions.
The Pakistani soldiers instead of going back , crossed the LOC and occupied the Indian posts. The Indian army was first informed about this Pakistani activities by the local shepherds.
The Indian army initially had absolutely no clue about the extent of infiltration by the Pakistani soldiers and sent a small patrol team of five soldiers led by Captain Saurabh Kalia to verify this information. This unit was ambushed by Pakistani soldiers who not only killed this entire unit but returned their mutilated bodies.

The Objective Of the Kargil War
The main objective of the Kargil war for Pakistan was to occupy the strategic locations along National highway NH-1D which connects the Srinagar and Leh. This NH 1D road is the main supply line for the Indian soldiers deployed in the Siachen Glacier. The Siachen area is the highest battlefield on the earth at altitude 6000 meters where India Army has been deployed to foil the Pakistani attempts to capture this strategically important Siachen area .
The Indian army controls the major part of the Siachen area. The Indian Army had launched operation Meghdoot in 1984 which gave the Indian army control over the majority of Siachen area. The Pakistani plan was to disrupt the NH-1D supply line so as to compel the Indian side to settle the Kashmir issue on terms favourable to Pakistan.
As stated by Pakistani Army Chief General Parvez Musharraf, the Kargil war was a revenge for the loss and humiliation suffered by Pakistan during India-Pakistan war 1971, in which Indian Army liberated Bangladesh which used to be East Pakistan.
The Scale Of Infiltration By Pakistani Army in Kargil War
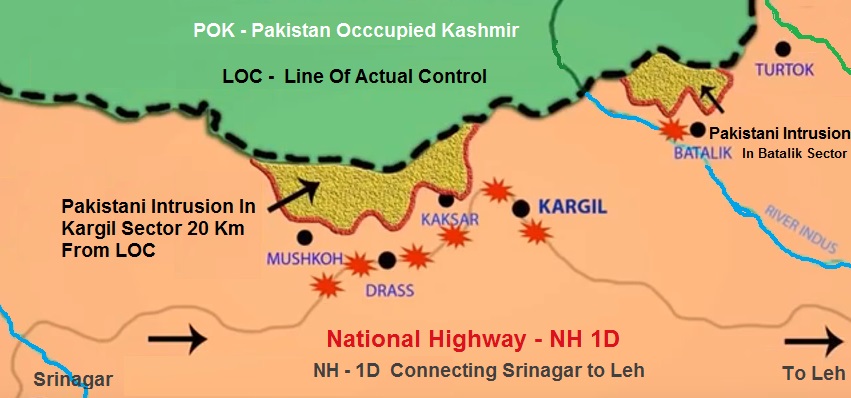
In order to assess the extent of infiltration by Pakistani troops, the Indian Air Force ( IAF ) used Canberra high altitude reconnaissance plane which confirmed the Pakistani infiltration along 150 km mountain range from Drass to Batalik and 20 KM inside the Indian territory from LOC.
The Pakistani troops had also fired with anti-aircraft guns on this plane which luckily escaped with minor damage and managed to successfully land with vital information.
Indian Army Operation In Kargil War
Operation Vijay Launched
The Indian Army responded to Pakistani infiltration across LOC by launching “Operation Vijay” and quickly mobilized 200000 soldiers. By now , the Indian army had sufficient information about the extent of infiltration by the Pakistan soldiers all along the LOC stretch of 150 Km. The Indian Air Force ( IAF ) had also conducted a number of sorties for reconnaissance and returned with vital information about the Pakistani activities and the details of the forward posts occupied by the Pakistani soldiers.
The crossing of LOC by Pakistani soldiers was a serious development and the Indian side viewed this as an act of war . The Indian army had quickly mobilized the army units and launched “Operation Vijay” with a massive counterattack to recapture these forward posts occupied by the Pakistani soldiers.
The Kargil district topography is one the most difficult hilly and inhospitable terrain in the world for any combat operation. The Pakistani soldiers had occupied some of the most strategically located posts located on the mountain peaks from where they could easily target NH-1D cutting off the Indian supply line.

It was a formidable challenge for the Indian army to first climb to these mountain peaks under the most hostile conditions along with the arms , ammunition and then carry out the attack to recapture these posts. Further , the real challenge was to carry out these attacks mostly during the night.
The Pakistani soldiers had occupied well-entrenched positions all along the strategically located mountain peaks such Tiger hill and Tololong . While climbing these mountain peaks , the Indian soldiers were continuously being fired upon by the Pakistani soldiers seating on the top of these mountain peaks .

The Pakistani soldiers had a major positional advantage of being located on these strategic locations on the mountain peaks. Whereas the Indian soldiers had a major disadvantage as they had to first climb to these mountains by directly exposing to the Pakistani fire. And for this reason, the Indian army initially suffered heavy casualties due to their venerability to the Pakistani fire.
The Indian army soon realized that they are no longer fighting militants but they are fighting with the Pakistani army regular soldiers , very well-equipped including the anti-aircraft weapons ( US Stinger Missiles). Throught the war , the Pakistani army denied the presence of their troops. The Pakistani army was providing artillery fire support to its soldiers firing from behind the LOC – line of control inside POK .
The Indian army extensively used the heavy artillery 155 mm howitzer guns Bofors FH-77 B which played a crucial role in providing artillery cover fire to the Indian soldiers before climbing these mountain peaks.
The Indian army continued the operation despite all odds and hostile conditions. The Indian army within a span of almost two months captured all the posts one-by-one from the Pakistani occupation and achieved victory in Kargil war.

Indian Air Force ( IAF ) Operation In Kargil War
Operation Safed Sagar
The Pakistani soldiers had managed to secure the positions on most of the heavily fortified bunkers located on the top of these mountains. The Pakistani soldiers were protected against the Indian artillery fire due to these fortified bunkers and the artillery fire was not very effective.
And therefore, The Indian Air Force ( IAF ) was called into action. The Indian air force launched Operation “Safed Sagar”. The primary objective for the Indian air force was to destroy these fortified bunkers, cut-off the Pakistani supply lines and to keep the Pakistani air force at bay.
The first phase of the air operation started with the rocket attack by using helicopters. During the Kargil war , the Indian Air Force MI-35 Hind Helicopter Gunship could not be used because it has not been designed for high altitude attack operations and cannot be used beyond 10,000 feet altitude. For high altitude attack operations, the IAF needed a lightweight attack helicopter which IAF acquired after the Kargil war .
And therefore, the Indian air force attempted to use MI-17 which is essentially a transport helicopter. The MI-17 was modified to carry rocket pods needed for the attack role and capable of flying at altitude up to 20,000 feet. However , MI-17 being a large size transport chopper lacked the agility required for high altitude combat roles.
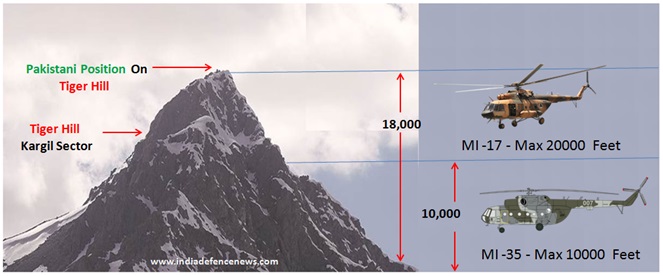
The Pakistani soldiers were equipped with US shoulder-fired Stinger Missiles and Indian Air Force lost one such MI-17 chopper during the attack along with crew of four crew members . The Indian Air Force suffered some losses during the initial phase and Pakistan forces managed to shoot down one Mi -17 , one Mig-21 and one Mig-27 .
The Indian Air Force launched the second phase of attack using sophisticated Mirage 2000 recently acquired from France . The Mirage 2000 were equipped with Israeli Laser Designation Pods and the Laser Guided Bombs. With Mirage 2000 in action, the IAF delivered a devastating blow to the Pakistani positions and supply depot using precision shooting with Israeli supplied Laser Guided Bombs.
Israeli help also played a crucial role during the Kargil war. As the war started , Israel came to India’s rescue and supplied precision shooting weapons like Laser Designation Pods , Laser Guided bombs and UAV for reconnaissance operations. India also deployed Russian origin Mig-29 equipped with BVR ( Beyond Visual Range ) missiles to keep the Pakistani Air Force away from the combat zone.

Who won the Kargil War ?
After almost two months of intense military operation, India finally achieved its main objective of evicting all the Pakistani soldiers and militants who had infiltrated into the Indian territory. And therefore India won the Kargil war .
The Pakistani side suffered heavy casualties and humiliation. Pakistani troops had to withdraw unconditionally back to the previous LOC positions. Pakistan grossly underestimated the Indian reaction.
India had lost 527 brave soldiers whereas Pakistan had lost 700 soldiers. However, the Pakistani media reported a much higher figure of 3000 for Pakistani soldiers killed in the Kargil war. Throught the war , Pakistan denied its involvement and refused to accept the bodies of the Pakistani soldiers.
Kargil War Heroes And Gallantry Awards
Like any other war, The Indian victory came with price and India had lost some of its finest soldiers who made supreme sacrifice in defending their motherland.

Kargil War Indian Army Heroes Grenadier Yogendra Yadav , Rifleman Sanjay Kumar , Capt Vikram Batra , Capt Manoj Pande
| No | Name | Medal | Regiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lt Balwan Singh | Mahavir Chakra | 18 Grenadiers |
| 2 | Grenadier Yogendra Singh Yadav | Param Vir Chakra | 18 Grenadiers |
| 3 | Major Rajesh Adhikari | Mahavir Chakra | 18 Grenadiers |
| 4 | Major Vivek Gupta, | Mahavir Chakra | 2 Rajputana Rifles |
| 5 | Naik Digendra Kumar | Mahavir Chakra | 2 Rajputana Rifles |
| 6 | Major Padmapani Acharya | Mahavir Chakra | 2 Rajputana Rifles |
| 7 | Captain Vikram Batra | Param Vir Chakra | 13 JAK Rifles |
| 8 | Rifleman Sanjay Kumar | Param Vir Chakra | 13 JAK Rifles |
| 9 | Captain Anuj Nayyar | Mahavir Chakra | 17 JAT Regiment |
| 10 | Lieutenant Manoj Kumar Pandey | Param Vir Chakra | 1/11 Gorkha Rifles |
| 11 | Captain Neikezhakuo Kenguruse | Mahavir Chakra | 2 Rajputana Rifles |
| 12 | Captain Haneef-u-ddin | Vir Chakra | 11 Rajputana Rifles |
| 13 | Squadron Leader Ajay Ahuja | Vir Chakra | Indian Air Force |
| 14 | Major Mariappan Saravanan | Vir Chakra | 1 Bihar Regiment |
| 15 | Naib Subedar Chuni Lal, | Ashok Chakra | 8 JAK Light Infantery |
International Reaction to Kargil war
US Reaction to Kargil War
The Kargil war was planned and executed by Pakistani army chief General Parvez Musharraf. It is believed that the Pakistani political leadership was not even consulted by General Parvez Musharraf before starting the military operation of this scale against India.
The Pakistani General grossly underestimated the Indian reaction to such invasion. When Pakistani forces started suffering heavy casualties, the Pakistani political leadership Prime Minister Nawaz Shariff rushed to US to seek intervention .
However , for the first time in India US relations, the US President Bill Clinton refused to intervene till Pakistani forces are not called back unconditionally to the earlier LOC position. The US administration refused to provide an honourable exit option for Pakistan . The heavy losses being suffered by Pakistan army compelled the Pakistani army to vacate all the occupied Indian posts and retreat back to the previous LOC position.

Chinese Reaction to Kargil War
Surprisingly, China took a neutral stand despite Pakistani Foreign Minister Sartaj Aziz hurried visit to China. However , China advised both the warring parties to reach a political settlement. Most countries supported the Indian stand and Pakistan was completely isolated being the aggressor and for crossing the LOC.
The Political Fallout Of Kargil War
Political Fallout In Pakistan
After the Kargil war defeat, the pressure started mounting on the Pakistani Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif to fix the accountability for a large number of causalities suffered by the Pakistani army and the political humiliation suffered due to Kargil war. The humiliating defeat suffered by Pakistan in Kargil war also spoiled the relations between the Pakistani political leadership and the Army.
Pakistani PM Nawaz Sharif was also very upset with General Parvez Musharraf for not consulting him before initiating war with India. The unrest between political leadership and the army chief eventually led to another coup by Pakistan army.

In a swift action on October 12th, 1999 , the Pakistani PM Nawaz Sharif dismissed General Musharraf when he was out of the country on a visit to Sri Lanka. He was also denied entry in Pakistan and the civilian government tried to prevent his plane from landing at the Karachi airport.
However , the Pakistani armed forces took over the control of the airport and other government installations. In a military coup, General Musharraf dissolved the parliament and dismissed the Sharif government.

Important Lessons Of Kargil War
Lesson for Pakistan
Pakistan has not learned any lesson in the past , nor it will learn in future . Pakistan’s obsession for the control over Kashmir has resulted into the continuous downfall of its economy . Pakistan has also become a fertile ground for terrorists and emerged as a serious security threat for the international community.
As usual , In 1971 India Pakistan war , Pakistan had even claimed victory when India had partitioned Pakistan into two parts and Indian army liberated Bangladesh from Pakistan. Pakistan army chief had signed Instrument of Surrender which includes surrender of 93000 Pakistani soldiers taken as prisoner of war from east Pakistan . But Pakistan always claims victory .
Lessons for India
Just a few months before the Kargil war 1999 , the Indian Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee had travelled to Lahore , Pakistan as an attempt to normalize the relations with Pakistan and to initiate a dialogue with Pakistan for the peaceful resolution of Kashmir issue. Despite these interactions, Pakistan army started Kargil operation.

The Kargil war exposed many critical gaps in India’s strategic planning and preparedness which includes :
- Need for Light Attack Helicopter for high altitude operations.
- Need for Satellite to Closely monitor boundary.
- Need to upgrade existing aircraft.
- Need to acquire the latest multirole Aircraft.
- Need to acquire precision munitions such as LGB.
- Need to acquire IAF heavy lift Transport capability.
Conclusion
The Kargil war was the fourth major armed conflict started by Pakistan in 1999. The Kargil war was planned and executed by Pakistan Army Chief along with his other three colleagues including Pakistan intelligence agency ISI. The Pakistan army had grossly underestimated the Indian response. India responded with major military and diplomatic offensive against Pakistani aggression.
The Indian army supported by Indian Air Force launched a major operation lasted for two months and at the end of the war , recaptured all the territory and posts occupied by the Pakistani forces. Pakistan army had suffered huge losses in terms of casualties and the political humiliation.
The Pakistans humiliating defeat in this Kargil war also triggered another military coup in Pakistan.
