The Indian Army Tanks – Latest Updates 2020
The Indian army is one of the largest and most well equipped professional armies in Asia .The main battle tank ( MBT ) is the primary weapon system for any army . The Indian army tank fleet mainly consists of a mix of both Soviet origin tanks as well as indigenously developed Indian main battle tanks .
The first breed Indian army tanks include T-54 , T-55 and the first indigenous Vijayanta tank. Both these tanks have already been phased out of army fleet . The legendary Russian T-72 tank , which Indian army operates in large numbers and still continues to be the mainstay of the Indian Army tank fleet .
The Indian Army also operates Arjun MBT which is India’s second indigenously designed and developed main battle tank ( MBT ) . The Indian Army Tanks also includes T-90 tanks ( Bhishma ) which is the latest addition to the Indian army . The T-90 tank is considered to be amongst the best Russian MBT .

The Indian Army T–54 And T-55 Tanks :
These tanks belong to the first generation of Soviet era tanks produced by the soviet union after the second world war . India acquired these tanks after independence in 1947 . These tanks were designed and manufactured by the soviet union from 1945 till 1958 and were mainly being used by Warsaw Pact Countries. The Indian Army no longer operates these tanks as they have been replaced with latest modern tanks .

The Indian Army has extensively used these tanks during India-Pakistan wars fought between the 1960s to the 1980s. Pakistan had attacked India in 1960 and 1965 and was defeated by the Indian armed forces .
The India- Pakistan war in 1971 witnessed a fierce tank battle at Basantar . An Indian armoured division and an armoured brigade of the Pakistan army fought intense tank battle . The Indian armoured brigade consisting mainly of T-55 and British Centurion tanks. The Pakistani brigade fought with relatively superior American made Patton tanks .
In this tank battle, Indian army’s 2nd Lieutenant Arun Khetarpal of the 17 Poona Horse stopped the Pakistani aggression . In a daring counter-attack, Lieutenant Arun Khetarpal led his 3 T-55s into the minefield area. After a fierce tank battle, many Pakistani Patton tanks were destroyed . The Pakistani After suffering heavy losses were forced to call for help from the 8th Armored Pakistan brigade.

In this tank battle , 2nd Lieutenant Arun Khetarpal and his team defeated the Pakistani attack and destroyed 10 Pakistani M48 Patton tanks .He himself destroyed 7 Patton tanks before he was killed in action. The casualties were heavily skewed against the Pakistani force with total 46 Pakistani tanks destroyed and India lost only 10 tanks. However, in this battle , 2nd Lieutenant Arun Khetarpal made supreme sacrifice for his country. He has been awarded Param Vir Chakra for his exemplary courage and valour.
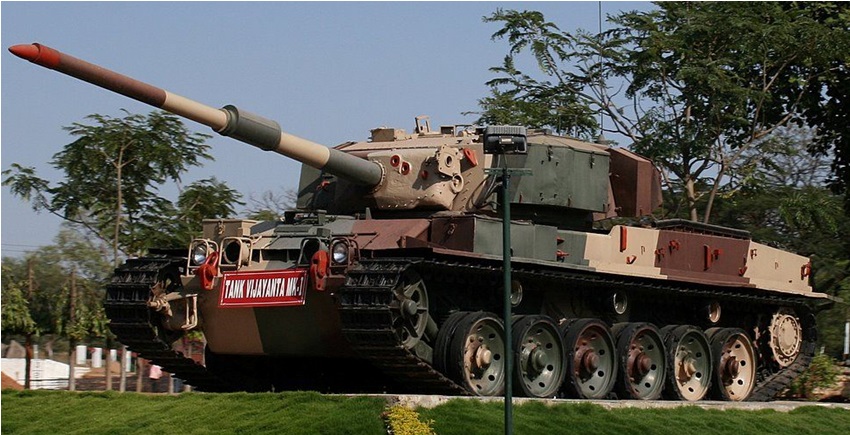
The Vijayanta Tank – India’s First Indigenous Tank
The Vijayanta tank was India’s first indigenously manufactured made in India main battel tank . The Vijayanta means victorious was derivative of British Vickers MK1 . The Vijayanta tank prototype design was completed in 1963 and the tank entered in to active service in 1965. The first batch of 90 Vijayanta tank was produced by Vickers in the UK .

The production line for these tanks subsequently started in India at Heavy Vehicles Factory ( HVF ) at Avadi in the state of Tamil Nadu. The HVF is a specialized manufacturing factory set up in 1961 by the Ordnance Factories Board, Government of India to manufacture heavy battlefield equipment such as infantry tanks and other armored vehicles .
The Vijayanta tank had gone through a number of upgrades many different varients were manufactured such as Mark 1A , 1B and 1C . The total number of Vijayanta tanks produced by HVF is estimated to be almost 2000 units . This tank was phased out of service from the Indian army by 2008 . The Vijayanta MK2 was the last upgrade .
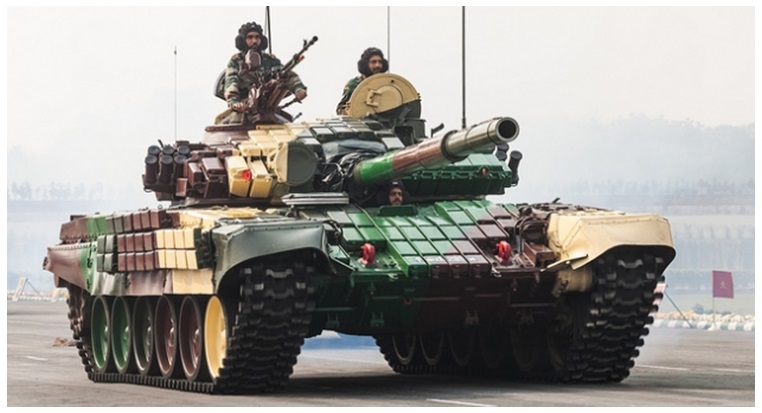
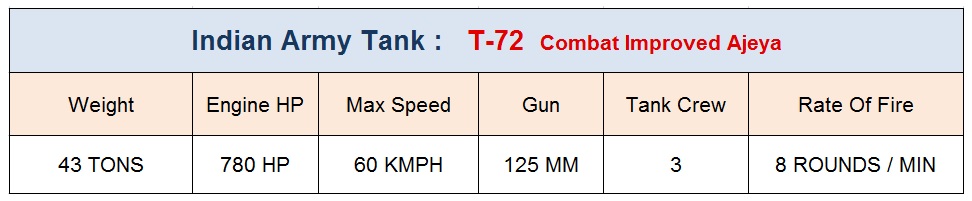
The Legendary T–72 Ajeya Tank
The legendary T-72 tank belongs to the second generation of Soviet modern tanks produced by the erstwhile soviet union during the cold war period . The T-72 tank first entered in to production in 1971 . The T-72 was one of the most widely exported tanks still currently in service with over 40 countries .
The Indian T-72 Ajeya Tank was manufactured under license production for Russian T-72M1 . The production started in the late 1970s at HVF Avadi . So far over 1800 tanks with different variants have been delivered to the Indian Army.
The T-72 continues to be the main stay of the Indian Army’s armoured Main Battle Tank ( MBT ) force which consists of 1,800 plus T-72M1 Ajeyas tanks . Intially India imported these tanks from the Soviet Union from 1982 to 1986 but later on, these tanks were produced locally by Heavy Vehicles Factory ( HVF ) at Avadi .

The Indian T-72 Features :
The T-72 tank is equipped with the 125 mm main gun which is capable of firing both standard main gun ammunition, including HEAT and APFSDS rounds. India has upgraded T-72 over the years.
The Indian T-72 Variants :
There are many variants of T-72 tanks.The T-72A first appeared in 1979, with thicker armor. Next came the T-72B in 1985, which incorporated features from the newer T-80. The T-72B variant had a laser rangefinder and thicker armor. The Indian army does not operate T-80 which is often confused with T-72 tank . The T-80 Tank is a totally different tank manufactured by different Russian factory.

The Indian T-72 CI Ajeya Upgradation :
India has been working on a long term up-gradation program for T-72 Ajeya’s in stages. The first stage of the upgrade is known as the “Combat Improved Ajeya”.
The second generation indigenous Arjun Tank was still under development and it felt necessary to upgrade the existing fleet of T-72 . As a part of T-72 CI Ajeya upgrade program , India purchased 300 Polish SKO-1T Fire Control Systems In 2002 .These were already being used on the polish PT-91 MBT. This kit had thermal imaging sight to enhance the night vision capability of the T-72 tanks .
The upgrade also include new “Explosive Reactive Armor” ( ERA ) developed by Defence Research & Development Organization ( DRDO ) , fire detection & suppression system within the crew compartment, new 81mm smoke grenade launchers mounted on the side of the turret and GPS.
As per the mid-2011 press release, India defence spokesman stated that 250 vehicles had so far been upgraded to the CI Ajeya.
New Engine for Indian T-72 Tanks 2018 :
India’s Ministry of Defense ( MoD ) has approved the procurement of 1000 new engines for the Indian Army’s T-72M1 Ajeya main battle tank ( MBT ) force. The majority of engines will be produced locally by technology transfer with foreign collaboration with the Engine Factory Avadi ( EFA ) ,
The EFA is a subdivision of the Ordnance Factories Board. The new engines for T-72 will significantly improve the tanks performance in terms of mobility, agility, and acceleration.
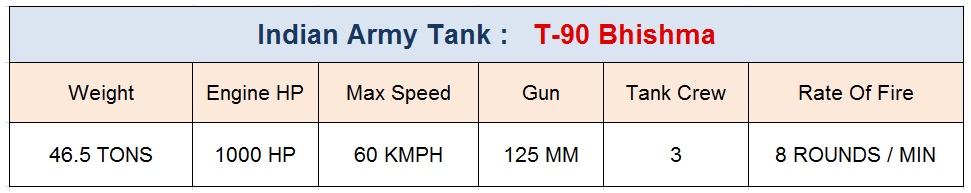
The Indian Army’s Latest T-90 Bhishma Tanks :
The Russian T-90 tanks was the latest addition to the Indian Army’s formidable tank fleet . The Russian army inducted T-90 tanks in 1992. The induction of these tanks in Indian army was a logical step as majority Indian army tanks have Russian origin .
India acquired first batch of T-90 tanks in February 2001 when Indian Army signed a contract for total 310 T-90S tanks. Out of these total , 124 tanks were to produced in Russia and the remaining were to be delivered in ‘knocked down’ form for its final assembly in Indian HVF Avadi .
The Indian army received the delivery of first T-90S MBT in January 2004. As per contract the HVF also started assembly of T-90 tanks in india at HVF Avadi . These locally assembled tanks are christened ‘Bhishma’.
The Indian T-90 tanks were fitted with the Shtora self-protection system and Catherine thermal imagers from Thales of France and Peleng of Belarus. The first batch of 10 T-90 Bhishma tanks were inducted into the Indian Army in August 2009. The Indian army intends to take the T-90 tank count to 2000 tanks by 2020 .

The T-90 Bhishma Technical Features :
The T-90 Upgrade Program :
The current main weapon of the T-90 tank is second generation laser guided INVAR Missile system . The Indian Army intends to replace the existing INVAR missiles with a third generation gun-launched missile.
The Indian army is now working on the project to equip the existing T-90 tanks with long-range anti-tank missiles in order to enhance the combat capability. This will significantly improve the T-90 strike range up to 8 KM with day and night capability .

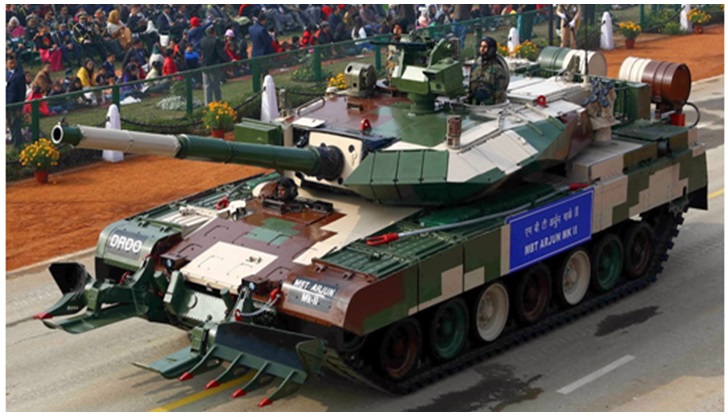
The Indian Army’s Indigenous Arjun Tank :
The Arjun tank is a third generation main battle tank designed and developed for the Indian Army . The Arjun tank has been designed by Indian DRDO ( Defence Research And Development Organization ( DRDO ) and Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment ( CVRDE).

The Arjun Tank Development :
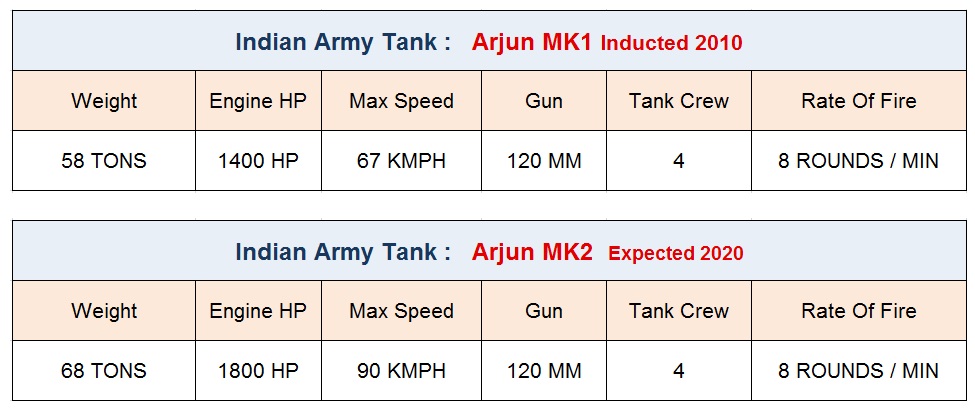
The Arjun tank development started in 1974 jointly by DRRO and CVRDE . The Indian army received the first batch of Arjun MK1 in the year 2010 after a prolonged development period of almost three decades . The Indian army is currently operating over 100 plus Arjun MK1 version tanks inducted in 45th armoured regiment of the Indian army .
However during the actual user field trials conducted by the Indian army under various battle conditions , several problems were noticed in the Arjun MK1 . And therefore Indian army could not induct Arjun MK1 in large numbers .
The Indian army has suggested 97 improvements in the Arjun MK1 prototype out of these 15 are major improvements . The DRDO is currently working on these 97 improvements specified by the Indian army .
These improvements have now been incorporated by DRDO in the Arjun MK2 version which is being evaluated by the army . However, the initial reports suggest that the Arjun MK2 weight of 68 Tons still continues to be a major concern area for the army which may cause logistical issues . The Arjun MK2 is expected to be ready for induction by 2020 .
The Arjun tank – Technical Specifications And Features :
Arjun Tank Mobility :
Arjun is powered by a German single MTU multi-fuel diesel engine which delivers 1400 HP . The tank transmission is also by German company RENK. The Arjun can cruse with maximum speed of 67 KMPH . The Arjun tank is one of the heaviest tanks in the world ( MK1 – 58 Tons , MK2 – 68 Tons ) which affects the mobility despite good engine power . This has been identified as one of the major area for improvement specified by the Indian Army which DRDO is working on .
Arjun Tank Firepower :
The main gun for the Arjun features a 120 mm rifled gun which can fire all standard ammunition and also the main gun fired missiles . The standard ammunition includes indigenously developed armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding-sabot ( APFSDS ) ammunition.
Arjun Tank Protection :
The Arjun tank is protected by “Kanchan” armour of type modular composite armour. The Kanchan armour has been indigenously developed by Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory ( DMRL ) . The Kanchan armour has been designed to defeat the APFDS and HEAT rounds fired at the tank . The Arjun tank also offers protection against mines . The Arjun tank crew is also protected against nuclear and biological attack .
The Arjun MK2 – New Main Battle Tank :
The DRDO is currently working on the development of new variant Arjun tank MK2. The Arjun MK2 will be based on the suggested improvements in the Arjun Mk1 . After extensive user trial evaluation of Arjun MK1 tanks , The Indian army has suggested 93 improvements out of which 13 are major improvements .
The Arjun MK2 has been designed with features of third generation tank . The DRDO has completed the design and development of Arjun MK2 in a record period of barely three years . During the evaluation conducted by the Indian army , The Arjun MK2 has performed very well as against T-72 and T-90 series Soviet tanks .
The Arjun MK2 incorporates the latest main battle tank technology which offers excellent firepower , mobility and protection to the tank crew . The Indian Ministry of defence apex decision-making body “Defence Acquisition Council” ( DAC ) has already approved the production of 118 Arjun MK2 tanks . These tanks will be produced in Heavy Vehicle Factory at Avadi .
However , The DRDO is still struggling to achieve a significant reduction in the weight Arjun MK2. Although Arjun MK2 has performed very well in protection during the user evaluation trials but the tank weight has increased from Arjun MK1 58 ton to Arjun MK2 68 tons . The Indian army is essentially looking for lightweight tanks which should not be more than 50 tons .
The Indian Army’s “Future Ready Combat Vehicles” :
The Indian army operates the substantial number of T-72 tanks which are due for retirement. And therefore, The Indian government has issued global RFI – Request For Information in 2016 for the procurement of 1770 FRCV – Future Ready Combat Vehicle.
The Indian Army is actively scanning options to procure the new main battle tank for the Indian army . This procurement is named as Future Ready Combat Vehicles ( FRCV ) . This procurement of FRCV will be under recently announced government policy framework Strategic Partnership ( SP ) model . As per this model , the foreign vendor has to collaborate with an Indian partner company .

The Indian Army Chief General Bipin Rawat has recently concluded his six-day visit to Russia . The procurement of 1770 FRCV was top on his agenda as Russian latest T-14 Armata tank is one of the key contender in this deal .
The main contenders for FRCV include the Russian T-14 Armata, the Ukrainian T-84 Oplot , the French Le Clerc, and the South Korean K2 Black Panther. The Indian Army and government seems to be taking the right steps to ensure the early induction of new main battle tanks for the Indian Army.
Another important requirment light weight tank needed for hilly terrain especialy along the China border . China has recently developed and deployed light weight tank in 35 ton category . DRDO is already working on the similar project to design a light weight tank for the Indian Army .
During India China War 1962 , the Chinese army was far better equipped. However, now Indian army armoured units quite well equipped with latest tanks in its inventory .
