Indian Army Ranks
The Indian army is one of the largest and oldest institutions in the country. The Indian army has a well-defined rank based hierarchical structure. A proper understanding of Indian Army Ranks is important especially for the aspirants of NDA , CDS , AFCAT and other competitive examinations. In this article, we will discuss in detail Army Ranks , Insignia , Hierarchy and command structure.
Indian Army
Indian army is the second-largest army in the world with a strength of almost 1.3 Million which includes 1,237,117 active personnel and 960,000 reserve personnel. The Indian army is 123 year old institution founded on 1st April 1895 during the British Rule over india .
The main objective and primary mission of the Indian Army is to defend the Indian State against external aggression, ensure National Security and integrity of India . The Indian army is also deployed in a situation for maintaining peace , law and order, and internal security within the country.
The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces which consist of Indian Army , Navy and Air Force .
The Indian Army is going through a process of modernization. The Indian army is being equipped with latest weapons such as latest tanks , artillery guns , SAM ( Surface To Air ) batteries and SSM ( Surface To Surface ) missiles.
Indian Army Command Structure :
The Indian Army operates on a regimental structure. The command structure within the Indian army is based on the rank and also the geographic location of the unit.
The Indian army’s command structure is operationally classified into four categories :
- Commissioned Officers.
- Junior Commissioned Officers ( JCO).
- Non-Commissioned Officers.
- Soldiers
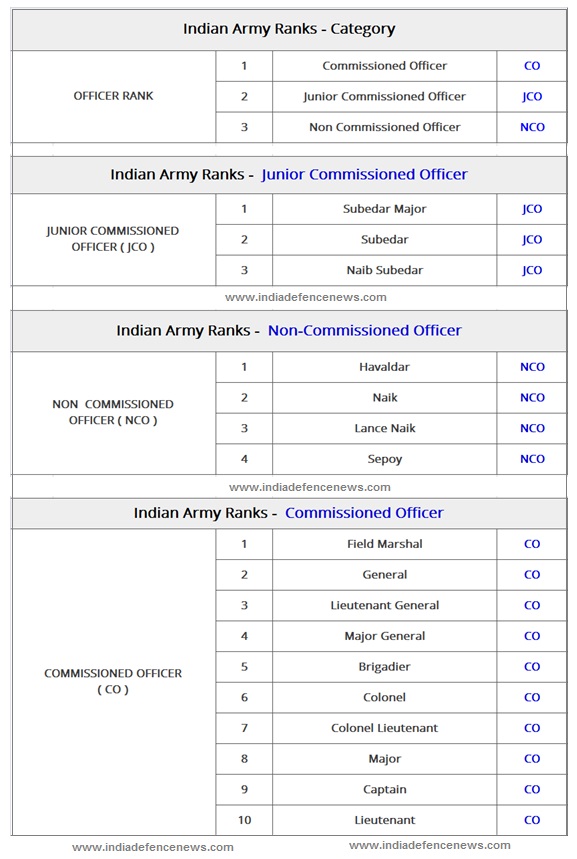
| Indian Army Ranks – Officer Category | ||||
| OFFICER RANK CATEGORY | 1 | Commissioned Officer | CO | |
| 2 | Junior Commissioned Officer | JCO | ||
| 3 | Non-Commissioned Officer | NCO | ||
The Indian army’s command structure is geographically divided into seven locations :
| No | INDIAN ARMY COMMAND | HEADQUARTER |
| 1 | Northern Command | Udhampur |
| 2 | Southern Command | Pune |
| 3 | Eastern Command | Kolkatta |
| 4 | Western Command | Chandimandir , Panchkula , Haryana |
| 5 | South Western Command | Jaipur |
| 6 | Central Command | Lucknow |
| 7 | Army Training Command | Shimla |
Commissioned And Non- Commissioned Officers
The Indian army distinguishes between commissioned and non-commissioned officers by their roles , On the job duties, respective ranks, the authority delegated and their pay scale structure.
Non-Commissioned Officer ( NCO ) :
The Non-Commissioned Officer ( NCO ) is an Indian military officer who has not earned a formal designation of commissioned Officer ( Also referred as Commission ) . The Non-Commissioned personnel usually perform duties based on specific skills such as training, recruitment , technical jobs or military policing. The NCO is considered to be the backbone of the army operations.
In the Indian army , the NCO can be promoted to JCO rank either from junior ranks based on the eligibility .
Commissioned Officer ( NCO ) :
The Commissioned officers are in the management cadre performing leadership roles. The Commissioned Officers provide the necessary direction and management expertise to perform various military operations on the ground . The CO’ s assign lower ranks NCO their duties , missions, their assignments and their orders. The NCOs are responsible to supervise lower ranks army personnel to ensure that the assignments are performed properly and get the job done.
In the Indian army, the JCO can be selected either from junior ranks based on the eligibility criterion Or directly through recruitment exams conducted.
Indian Army Ranks – Commissioned Officers
| Indian Army Ranks – Commissioned Officer | ||||
| COMMISSIONED OFFICER ( CO ) | 1 | Field Marshal | CO | |
| 2 | General | CO | ||
| 3 | Lieutenant General | CO | ||
| 4 | Major General | CO | ||
| 5 | Brigadier | CO | ||
| 6 | Colonel | CO | ||
| 7 | Colonel Lieutenant | CO | ||
| 8 | Major | CO | ||
| 9 | Captain | CO | ||
| 10 | Lieutenant | CO | ||
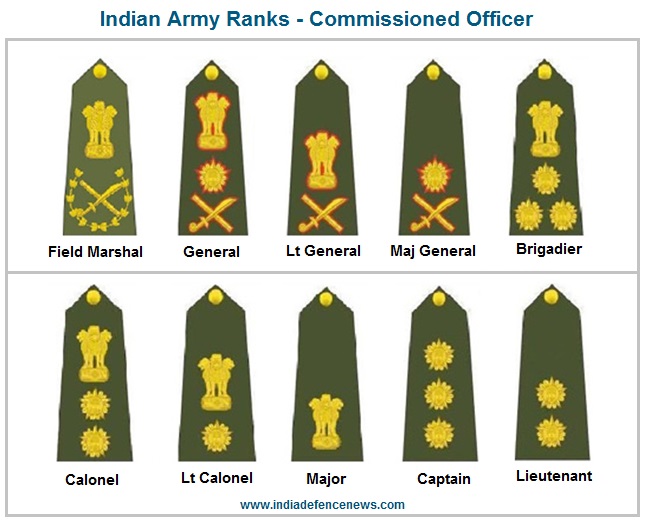

Indian Army Highest Rank – Field Marshal
Insignia – National emblem over a crossed baton and sabre in a lotus blossom wreath
The Field Marshal rank is the highest ceremonial rank in the Indian Army. The Field Marshal Rank is awarded in recognition of extemporary service to the Indian Army . As of now , in Indian army, only two officers have been elevated to the rank of Field Marshal and these officers include Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw and Field Marshal KM Cariappa .

The Field Marshal KM Cariappa was the first commander in chief of the Indian Army elevated as Field Marshal. He was Chief of Army staff during the first India Pakistan war just after the independence in the year 1947 . In this war , the Indian army defeated the Pakistani army and stopped the Pakistani forces from capturing the Indian Kashmir . This war is also referred to as the first Kashmir war.
The Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw became the second chief of the Indian Army who has been elevated to the ceremonial rank of Field Marshal. He was Chief of Army staff during the second India-Pakistan war in the year 1971 . In this war , Indian army defeated the Pakistani army and liberated Bangladesh as an independent country . This war is also referred to as the Bangladesh Liberation war.
Indian Army Rank : General ( COAS – Chief Of Army Staff )
Insignia For COAS : National emblem over a five-pointed star, both over a crossed baton and saber
This rank is operationally the highest rank held by an Army officer who is generally the Chief Of Army Staff ( COAS ) . This rank is considered to be an equivalent of cabinet secretary. General Bipin Rawat is currently holding the charge of COAS .
COAS Retirement : The retirement age for COAS is either 3 years after being appointed as COAS OR at the age of 62 years , whichever is earlier .
Indian Army Rank – Lieutenant General
Insignia For LG : National emblem over crossed baton and saber
The Indian army appoints Lieutenant Generals only by selection and the eligibility criterion is after completing 36 years of commissioned service in the Indian Army . the Lieutenant General may hold the position of a Vice Chief of Army Staff ( VCAS ) or Army Commander.
Retirement : The retirement age for Lieutenant General Rank Officer is 60 years.
Indian Army Rank – Major General
Insignia : Five-pointed star over crossed baton and sabre.
The Indian army Major Generals ( Abbreviated As MG / Maj Gen ) are promoted from commissioned officers by selection . The eligibility criterion for MG rank is 32 years of service as a commissioned officer in service with the Indian army .
Retirement : The retirement age for Major General Rank Officer is 58 years .
Indian Army Rank – Brigadier
Insignia : National emblem over three five-pointed stars in a triangular formation
The Indian army appoints Brigadier through the selection process. The eligible commissioned officers are promoted by selection . The eligibility criterion for Brigadier rank is 25 years of service as a commissioned officer in service with the Indian army .
Retirement : The retirement age for Brigadier rank officer is 56 years .
Indian Army Rank – Colonel
Insignia : National emblem over two five-pointed stars
The Colonels in the Indian army are promoted by the selection process . The eligibility criterion for Colonel Rank Officer is after 15 years of service as commissioned Officer OR eligible officer may be promoted on seniority basis after completing 26 years as a commissioned Officer with Indian Army . However, the officers promoted on Time-scale Colonels may hold the portfolio of a Lt. Colonel.
Retirement : The retirement age for Colonel rank officer is 54 years .
Indian Army Rank – Lieutenant Colonel
Insignia : National emblem over five-pointed star.
The Lieutenant Colonels in the Indian army are promoted by the selection process . The eligibility criterion for Lieutenant Colonel Rank Officer is after 13 years of service as a commissioned Officer and subject to clearance of Part D exam. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply “colonel” in conversation and also in unofficial correspondence.
Indian Army Rank – Major
Insignia : National emblem
The Indian army appoints Major through the selection process and time-bound promotion on completion of at least 6 years commissioned service with the Indian army .
Indian Army Rank – Captain
Insignia : Three five-pointed stars
The Indian army appoints Captain through the selection process and a time-bound promotion on completion of at least 2 years commissioned service with the Indian army .
Indian Army Rank – Lieutenant
Insignia : Two five-pointed stars
The Indian army appoints Lieutenant on commissioning into the Indian Army as an Officer.
Indian Army Rank – Junior Commissioned Officers ( JCO )
| Indian Army Ranks – Junior Commissioned Officer | ||||
| JUNIOR COMMISSIONED OFFICER ( JCO ) | 1 | Subedar Major | JCO | |
| 2 | Subedar | JCO | ||
| 3 | Naib Subedar | JCO | ||

Indian Army Rank – Subedar Major ( Infantry )
OR Risaldar Major ( Cavalry And Armored Regiments )
Insignia : Gold national emblem with stripe
The Indian army appoints Subedar Major Or Risaldar Major either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates .
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 34 years service or at the age of 54 years , whichever is earlier.
Indian Army Rank – Subedar ( Infantry )
OR Risaldar ( Cavalry And Armored Regiments )
Insignia : Two gold stars with stripe
The Indian army appoints Subedar Or Risaldar either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates .
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 30 years service or at the age of 52 years , whichever is earlier.
Indian Army Rank – Naib Subedar ( Infantry )
OR Naib Risaldar ( Cavalry And Armored Regiments )
Insignia : One gold star with stripe
The Indian army appoints Naib Subedar Or Naib Risaldar either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates Promotion by selection
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 28 years service or at the age of 52 years , whichever is earlier.
Indian Army Ranks – Non-Commissioned Officers
| Indian Army Ranks – Non-Commissioned Officer | ||||
| NON-COMMISSIONED OFFICER ( NCO ) | 1 | Havaldar | NCO | |
| 2 | Naik | NCO | ||
| 3 | Lance Naik | NCO | ||
| 4 | Sepoy | NCO | ||

Indian Army Rank – Havildar (Infantry)
OR Daffadar ( Cavalry and Armored Regiments )
Insignia : Three rank chevrons
The Indian army appoints Havildar Or Daffadar either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates Promotion by selection
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 26 years service or at the age of 49 years , whichever is earlier.
Indian Army Rank – Naik ( Infantry )
OR Lance Daffadar (Cavalry and Armoured Regiments)
Insignia : Two rank chevrons
The Indian army appoints Naik Or Daffadar either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates Promotion by selection.
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 24 years service or at the age of 49 years , whichever is earlier.
Indian Army Rank – Lance Naik ( Infantry )
OR Acting Lance Daffadar ( Cavalry and Armored Regiments )
Insignia : One rank chevron
The Indian army appoints Lance Naik Or Lance Daffadar either by promotion Or by selection amongst eligible candidates Promotion by selection.
Retirement : The retirement age is after completing 22 years service or at the age of 48 years , whichever is earlier .
Indian Army Soldiers
Indian Army Rank – Sepoy
Insignia – Plain shoulder badge
The Indian Army Sepoys are identified depending upon the Corps that they are assigned. For example,
- A Sepoy working in Signals will be called as Signalman.
- A Sepoy working in Infantry will be called as Rifleman.
- A Sepoy working in the Armored Corps is called as Gunner.
Watch Indian Army Ranks And Command Structure Explained
Watch Indian Army Ranks And Command Structure Explained ( HINDI )
Indian Army Rank Structure At A Glance :